Amazing animal facts 2024: Welcome to the fascinating world of animals, where every creature has its own unique story to tell. In this article, we dive deep into the top 10 amazing animal facts you probably didn’t know in 2024. These incredible insights will not only captivate your imagination but also highlight the wonders of nature’s ingenuity. Buckle up for a journey through the animal kingdom, filled with extraordinary abilities and behaviors that outshine our human senses.
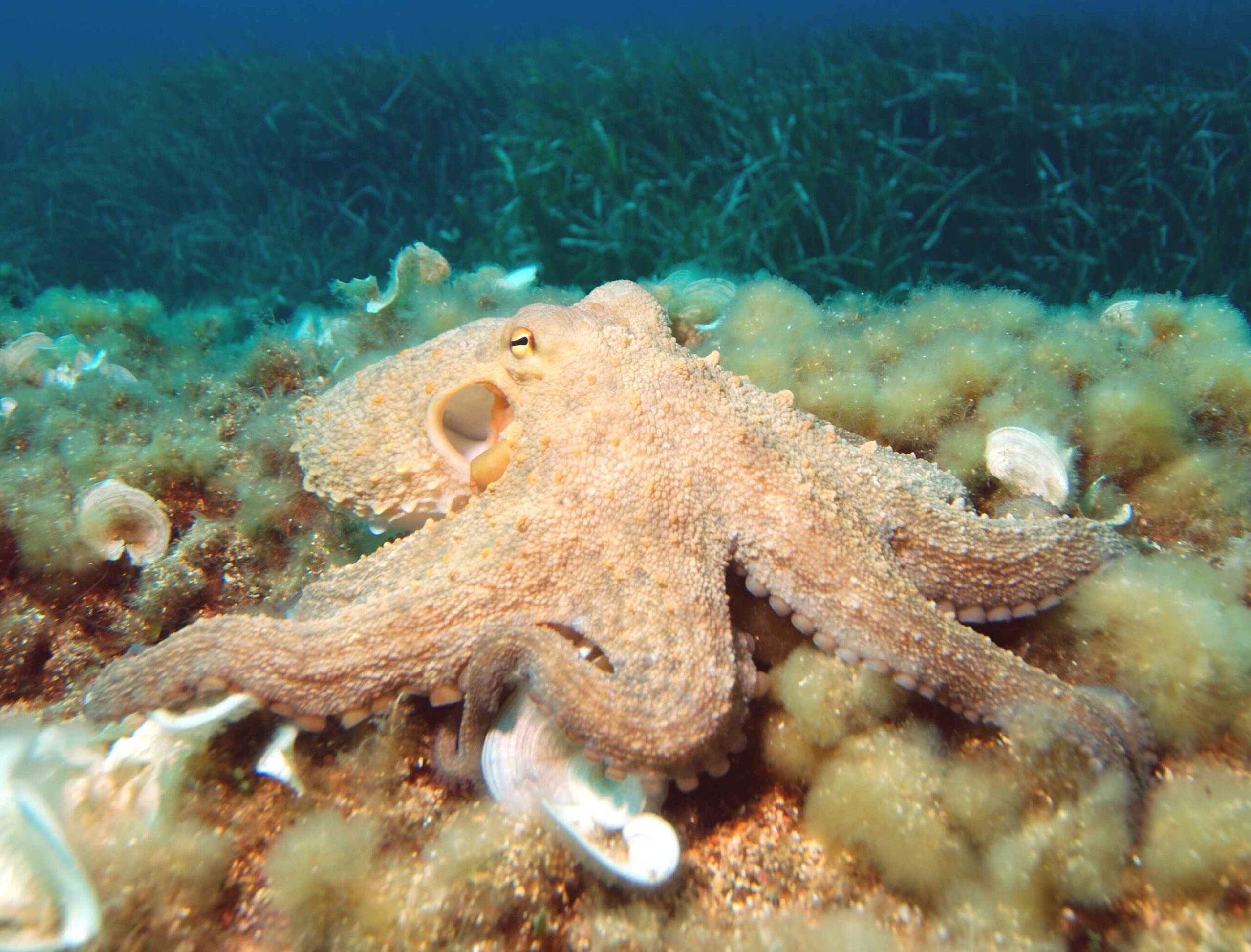
1. Octopuses Have Three Hearts
Engaging Fact
Did you know that octopuses have three hearts? Two of these hearts pump blood to the gills, while the third heart pumps it to the rest of the body. This unique circulatory system enables them to thrive in deep, oxygen-poor waters.
Human Comparison
Humans have a single heart that performs all circulatory functions. The octopus’s multiple hearts allow for more efficient oxygenation, which is crucial for their survival in the ocean depths. This extraordinary adaptation makes them incredibly agile and resilient in their underwater environment.
Why It’s Important
The unique circulatory system of octopuses highlights their remarkable adaptability to their deep-sea environment, showcasing the complexity of marine life.

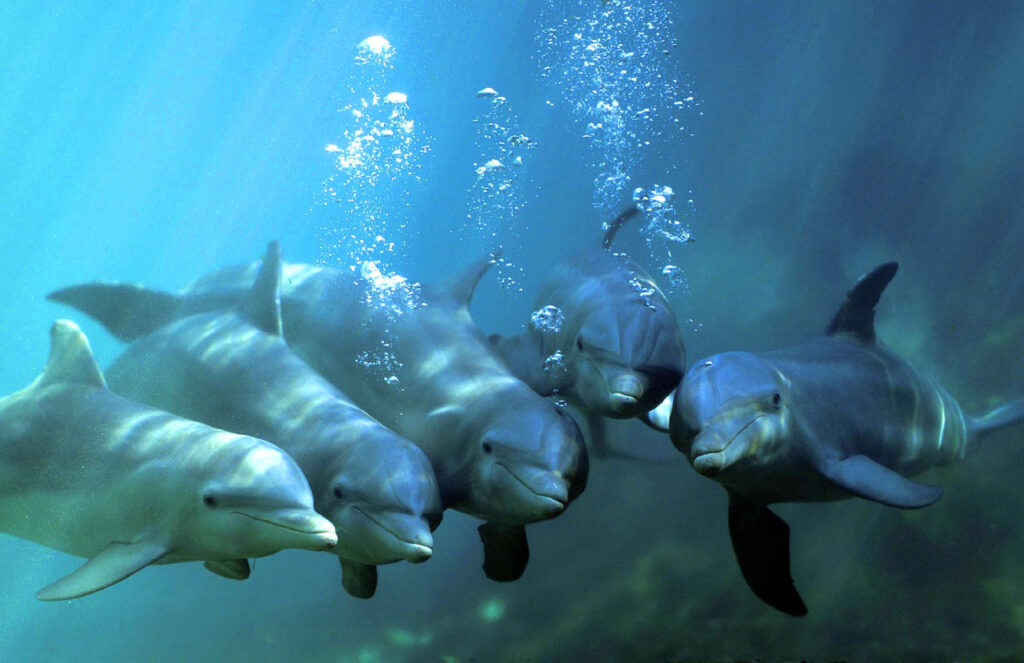
2. Dolphins Have Names
Engaging Fact
Dolphins use unique whistles to identify and call each other, effectively giving themselves names. Each dolphin’s “signature whistle” is distinct, similar to human names.
Human Comparison
Just like humans, who use spoken language and names for identification, dolphins’ use of signature whistles highlights their sophisticated communication skills and social structures. This ability is essential for their complex social interactions and group cohesion.
Why It’s Important
This ability indicates the advanced social structures and cognitive abilities of dolphins, shedding light on their complex behavior and intelligence.

3. Tardigrades: The Indestructible Creatures
Engaging Fact
Tardigrades, also known as water bears, can survive extreme conditions that would be lethal to most life forms. They can endure extreme temperatures, radiation, and even the vacuum of space.
Human Comparison
Humans are sensitive to extreme conditions and can only survive within a narrow range of environments. Tardigrades’ ability to enter a cryptobiotic state allows them to withstand environments that are otherwise uninhabitable, showcasing their unparalleled resilience.
Why It’s Important
The resilience of tardigrades demonstrates the incredible adaptability of life, providing insights into the potential for life to exist in extreme environments, including outer space.

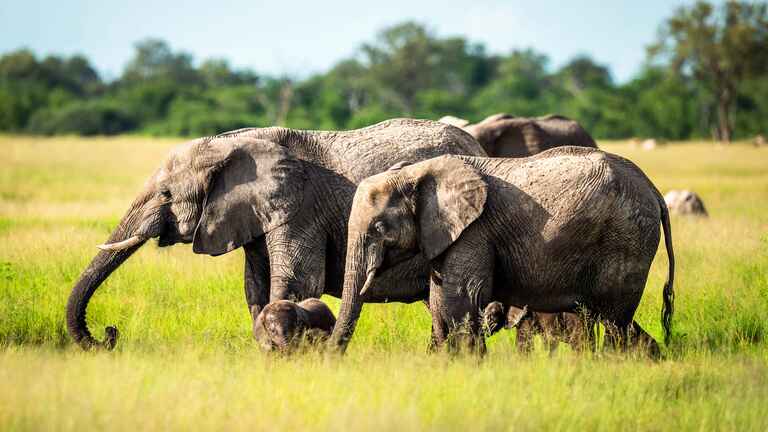
4. Elephants Can “Hear” with Their Feet
Engaging Fact
Elephants can detect vibrations through their feet. This ability helps them sense distant thunderstorms and communicate with other elephants using seismic signals.
Human Comparison
Humans rely on their ears for hearing, whereas elephants’ ability to “hear” with their feet demonstrates their remarkable adaptation to their environment. This skill allows them to detect distant events and maintain social bonds over vast distances.
Why It’s Important
Understanding this ability helps in the conservation and protection of elephants by recognizing the complexity of their communication and social behaviors.

Introducing the OnePlus Nord 4
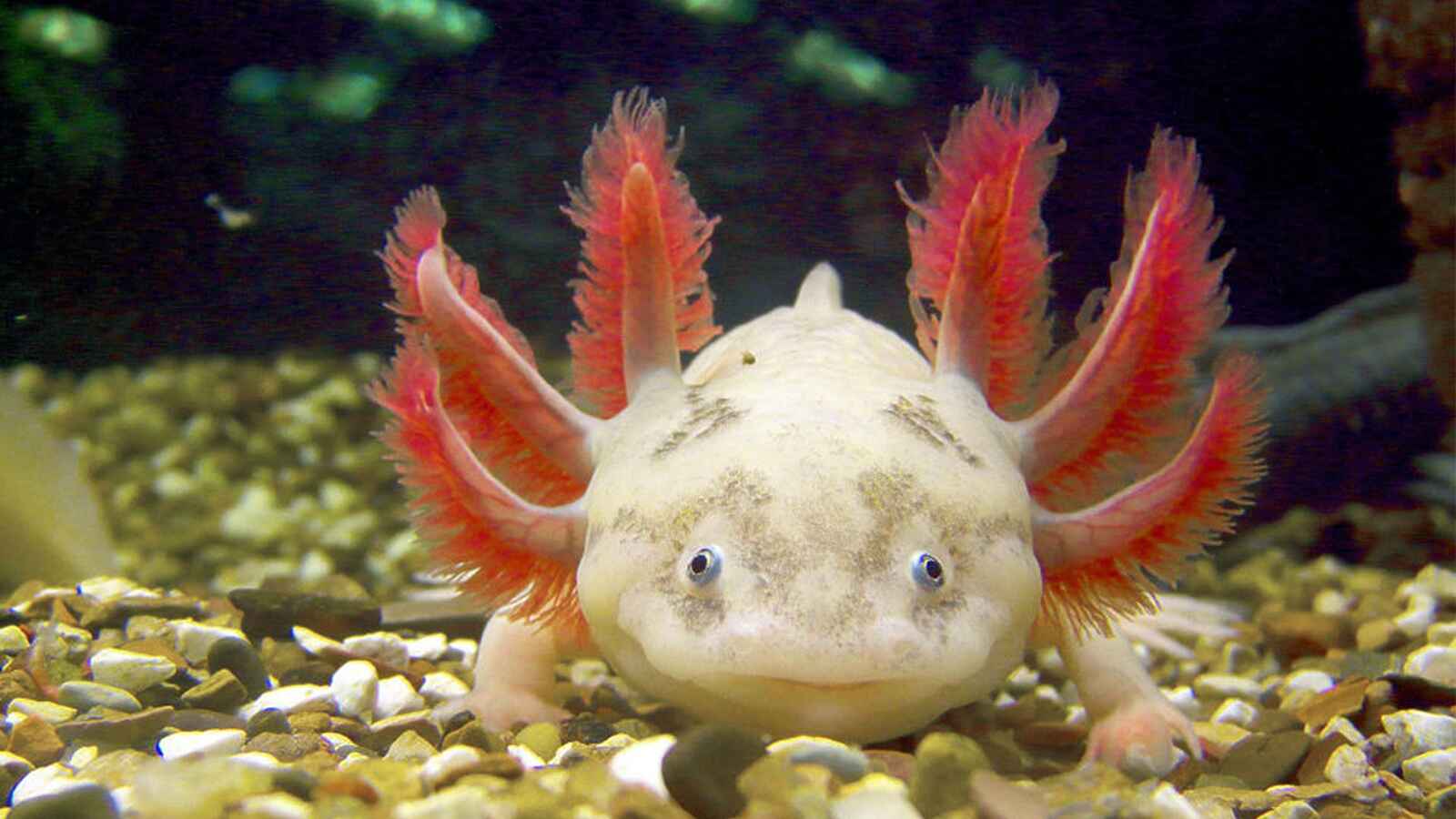
5. Axolotls Can Regenerate Their Body Parts
Engaging Fact
Axolotls, a type of salamander, can regenerate lost limbs, spinal cord, heart, and even parts of their brain. This remarkable regenerative ability has made them a focal point of biological research.
Human Comparison
Humans have limited regenerative abilities, such as healing small cuts or regenerating the liver to some extent. The axolotl’s extensive regenerative capacity offers insights into potential medical advancements for human tissue regeneration.
Why It’s Important
Research into axolotls’ regenerative abilities could lead to breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, potentially enabling humans to recover from injuries more effectively.

6. Pigeons Can Recognize Themselves in Mirrors
Engaging Fact
Pigeons have the ability to recognize their own reflection in a mirror, a trait usually associated with higher intelligence and self-awareness.
Human Comparison
Humans, along with a few other animals like primates and dolphins, possess self-recognition abilities. The pigeon’s capacity for self-awareness challenges the conventional understanding of avian intelligence.
Why It’s Important
This finding encourages a reevaluation of avian intelligence and cognition, influencing how we study and interact with birds.

7. Mantis Shrimp Punch with the Speed of a Bullet
Engaging Fact
The mantis shrimp can punch with the acceleration of a bullet from a gun, delivering blows powerful enough to break glass. This makes them one of the fastest and most powerful predators relative to their size.
Human Comparison
Humans cannot generate such extreme force in such a small area. The mantis shrimp’s punch, powered by specialized limbs and muscles, is an extraordinary example of natural weaponry and biomechanics.
Why It’s Important
The mantis shrimp’s punch demonstrates the extremes of biological evolution, providing insights into the mechanics of movement and the potential for bio-inspired engineering.

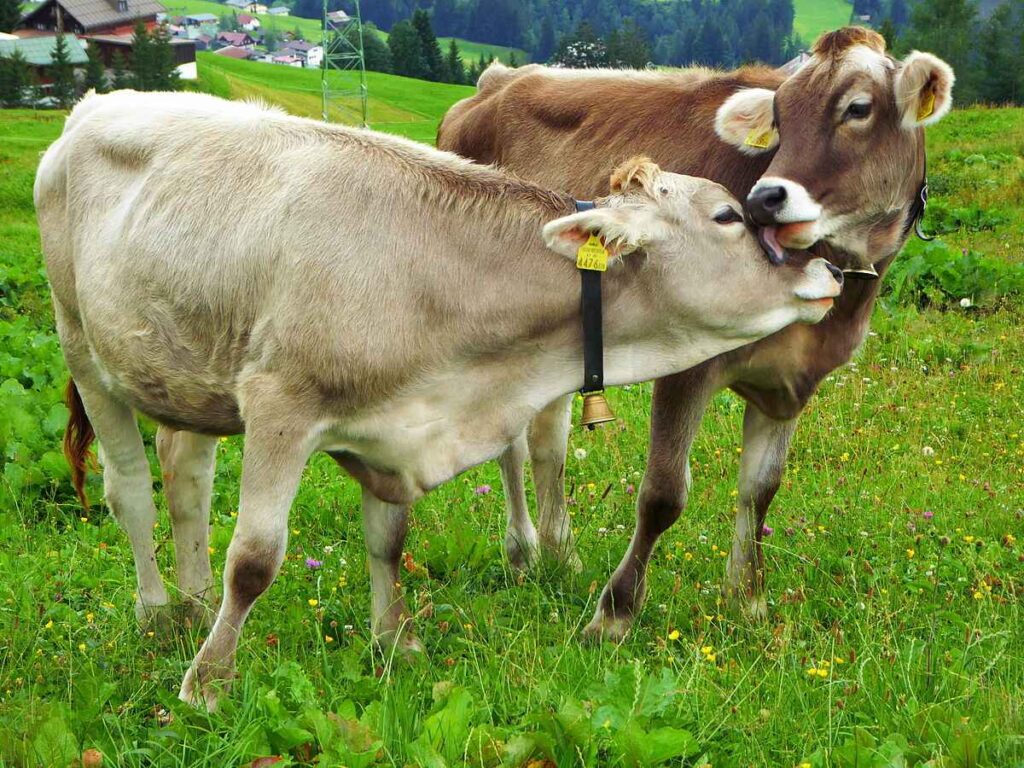
8. Cows Have Best Friends
Engaging Fact
Studies have shown that cows form close bonds with specific individuals in their herd, often referred to as their “best friends.” When separated from these friends, cows show signs of stress.
Human Comparison
Similar to humans, who form close relationships and experience stress when separated from loved ones, cows’ social bonds indicate their capacity for emotional connections and social complexity.
Why It’s Important
Recognizing the social bonds of cows can improve animal welfare practices in farming and husbandry, ensuring better treatment and care for these animals.

9. Honeybees Can Recognize Human Faces
Engaging Fact
Honeybees have the ability to recognize and remember human faces. They use this skill to differentiate between friendly and threatening humans.
Human Comparison
Humans rely on facial recognition as a fundamental social skill. Honeybees’ ability to recognize faces highlights their advanced visual processing capabilities and their importance in maintaining social harmony within the hive.
Why It’s Important
Understanding this ability helps in the development of better conservation strategies for bees, which are crucial pollinators in many ecosystems.

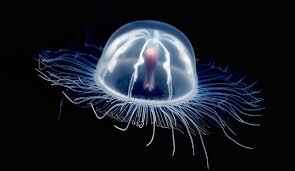
10. The Immortal Jellyfish
Engaging Fact
The Turritopsis dohrnii, also known as the “immortal jellyfish,” can revert back to its juvenile form after reaching maturity, essentially resetting its life cycle and avoiding death from old age.
Human Comparison
Humans age and eventually die, but the immortal jellyfish’s unique ability to reverse its life cycle offers intriguing possibilities for studying aging and longevity, potentially leading to breakthroughs in understanding human aging.
Why It’s Important
The study of the immortal jellyfish could revolutionize our understanding of aging and immortality, potentially leading to advancements in extending human lifespan.
Conclusion
The animal kingdom is filled with extraordinary creatures and astonishing behaviors that continue to surprise and intrigue us. From the regenerative abilities of axolotls to the self-awareness of pigeons, these amazing animal facts remind us of the incredible diversity and complexity of life on Earth. Keep exploring and stay curious, as there’s always more to learn about the fascinating world of animals.
